Secure your data with Google Identity and Neon Authorize
Implement Row-level Security policies in Postgres using Google Identity and Neon Authorize
What You'll Learn
Google Identity integration
JWT authentication setup
Row-Level Security policies
Use Google Identity with Neon Authorize to add secure, database-level authorization to your application. This guide assumes you already have an application using Google Identity for user authentication. It shows you how to integrate Google Identity with Neon Authorize, then provides sample Row-level Security (RLS) policies to help you model your own application schema.
How it works
Google Identity handles user authentication by generating JSON Web Tokens (JWTs), which are securely passed to Neon Authorize. Neon Authorize validates these tokens and uses the embedded user identity metadata to enforce the Row-Level Security policies that you define directly in Postgres, securing database queries based on that user identity. This authorization flow is made possible using the Postgres extension pg_session_jwt.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this guide, you will need:
- A Neon account. Sign up at Neon if you don't have one.
- To use Google Cloud Platform services, you'll need OAuth credentials. If you haven't set them up, follow the quickstart or these steps:
- Go to Google Cloud Console and create a new project if needed
- Navigate to APIs & Services > Credentials
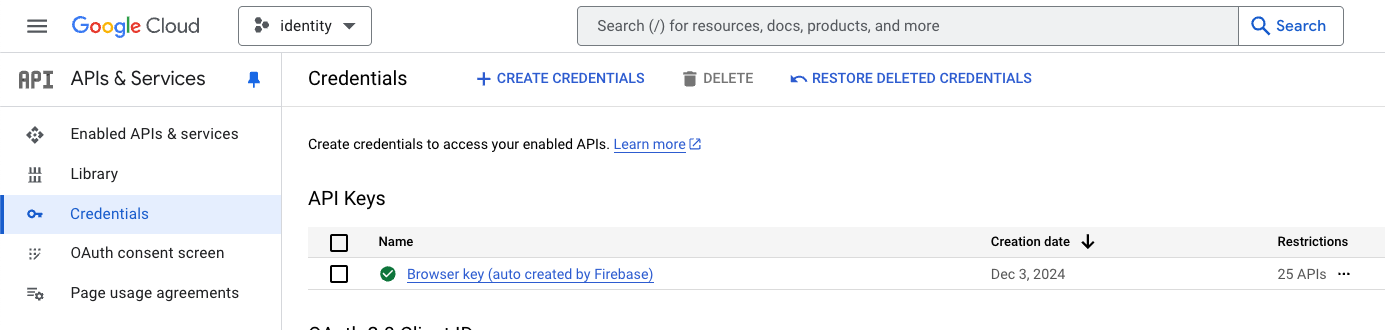
- Click Create Credentials and select OAuth 2.0 Client ID
- Set application type to Web application
- Add
http://localhost:3000/api/auth/callback/googleto Authorized redirect URIsNote
Replace the redirect URI with your application's callback URL, depending on your framework and environment.
- Save your
Client IDandClient Secretfor later use
Integrate Google Identity with Neon Authorize
In this first set of steps, we'll integrate Google Identity as an authorization provider in Neon. When these steps are complete, Google Identity will start passing JWTs to your Neon database, which you can then use to create policies.
1. Get your Google Identity JWKS URL
When integrating Google Identity with Neon, you'll need to provide the JWKS (JSON Web Key Set) URL. This allows your database to validate the JWT tokens and extract the user_id for use in RLS policies.
The Google Identity JWKS URL is:
https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/certsNote
For the JWT Audience value required by Neon Authorize, you'll use the OAuth 2.0 Client ID which was saved earlier.
2. Add Google Identity as an authorization provider in the Neon Console
Once you have the JWKS URL, go to the Neon Console and add Google Identity as an authentication provider under the Authorize page. Paste the JWKS URL and Google Identity will be automatically recognized and selected. Add your OAuth 2.0 Client ID as the JWT Audience value and click Set Up.
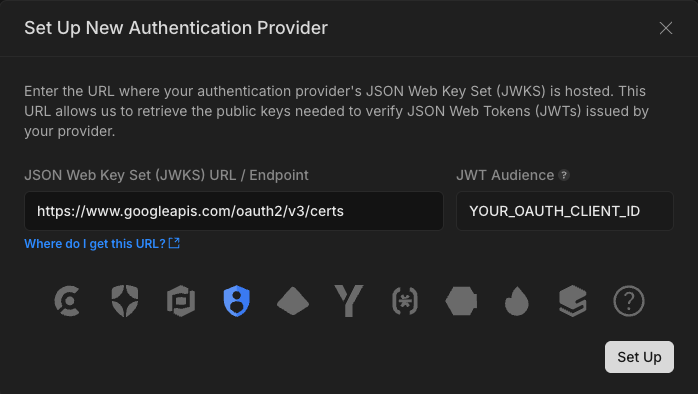
At this point, you can use the Get Started setup steps from the Authorize page in Neon to complete the setup — this guide is modeled on those steps. Or feel free to keep following along in this guide, where we'll give you a bit more context.
3. Install the pg_session_jwt extension in your database
Neon Authorize uses the pg_session_jwt extension to handle authenticated sessions through JSON Web Tokens (JWTs). This extension allows secure transmission of authentication data from your application to Postgres, where you can enforce Row-Level Security (RLS) policies based on the user's identity.
To install the extension in the neondb database, run:
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_session_jwt;4. Set up Postgres roles
The integration creates the authenticated and anonymous roles for you. Let's define table-level permissions for these roles. To allow both roles to read and write to tables in your public schema, run:
-- For existing tables
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE ON ALL TABLES
IN SCHEMA public
to authenticated;
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE ON ALL TABLES
IN SCHEMA public
to anonymous;
-- For future tables
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES
IN SCHEMA public
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE ON TABLES
TO authenticated;
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES
IN SCHEMA public
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE ON TABLES
TO anonymous;
-- Grant USAGE on "public" schema
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO authenticated;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO anonymous;- Authenticated role: This role is intended for users who are logged in. Your application should send the authorization token when connecting using this role.
- Anonymous role: This role is intended for users who are not logged in. It should allow limited access, such as reading public content (e.g., blog posts) without authentication.
5. Install the Neon Serverless Driver
Neon's Serverless Driver manages the connection between your application and the Neon Postgres database. For Neon Authorize, you must use HTTP. While it is technically possible to access the HTTP API without using our driver, we recommend using the driver for best performance. The driver also supports WebSockets and TCP connections, so make sure you use the HTTP method when working with Neon Authorize.
Install it using the following command:
npm install @neondatabase/serverlessTo learn more about the driver, see Neon Serverless Driver.
6. Set up environment variables
Here is an example of setting up administrative and authenticated database connections in your .env file. Copy the connection strings for both the neondb_owner and authenticated roles. You can find them from Connection Details in the Neon Console, or using the Neon CLI:
neonctl connection-string --role-name neondb_owner
neonctl connection-string --role-name authenticatedAdd these to your .env file along with your Google OAuth credentials:
# Database owner connection string
DATABASE_URL='<DB_OWNER_CONNECTION_STRING>'
# Neon "authenticated" role connection string
DATABASE_AUTHENTICATED_URL='<AUTHENTICATED_CONNECTION_STRING>'
# Google OAuth credentials
GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID='<YOUR_GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID>'
GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET='<YOUR_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET>'The DATABASE_URL is intended for admin tasks and can run any query while the DATABASE_AUTHENTICATED_URL should be used for connections from authorized users, where you pass the required authorization token.
Add RLS policies
Now that you've integrated Google Identity with Neon Authorize, you can securely pass JWTs to your Neon database. Let's start looking at how to add RLS policies to your schema and how you can execute authenticated queries from your application.
1. Add Row-Level Security policies
Here are examples of implementing RLS policies for a todos table – the Drizzle example leverages the simplified crudPolicy function, while the SQL example demonstrates the use of individual RLS policies.
import { InferSelectModel, sql } from 'drizzle-orm';
import { bigint, boolean, pgTable, text, timestamp } from 'drizzle-orm/pg-core';
import { authenticatedRole, authUid, crudPolicy } from 'drizzle-orm/neon';
// schema for TODOs table
export const todos = pgTable(
'todos',
{
id: bigint('id', { mode: 'bigint' }).primaryKey().generatedByDefaultAsIdentity(),
userId: text('user_id')
.notNull()
.default(sql`(auth.user_id())`),
task: text('task').notNull(),
isComplete: boolean('is_complete').notNull().default(false),
insertedAt: timestamp('inserted_at', { withTimezone: true }).defaultNow().notNull(),
},
// Create RLS policy for the table
(table) => [
crudPolicy({
role: authenticatedRole,
read: authUid(table.userId),
modify: authUid(table.userId),
}),
]
);
export type Todo = InferSelectModel<typeof todos>;The crudPolicy function simplifies policy creation by generating all necessary CRUD policies with a single declaration.
2. Run your first authorized query
With RLS policies in place, you can now query the database using JWTs from Google Identity, restricting access based on the user's identity. Here's how to run authenticated queries from both the backend and the frontend of our application using Google Identity Tokens. Highlighted lines in the code samples emphasize key actions related to authentication and querying.
'use server';
import { neon } from '@neondatabase/serverless';
import { getGoogleSession } from '@/lib/auth'
export default async function TodoList() {
const session = await getGoogleSession();
if (!session) {
throw new Error('No session available');
}
const sql = neon(process.env.DATABASE_AUTHENTICATED_URL!, {
authToken: async () => {
const jwt = session.id_token;
if (!jwt) {
throw new Error('No JWT token available');
}
return jwt;
},
});
// WHERE filter is optional because of RLS.
// But we send it anyway for performance reasons.
const todos = await
sql('SELECT * FROM todos WHERE user_id = auth.user_id()');
return (
<ul>
{todos.map((todo) => (
<li key={todo.id}>{todo.task}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}